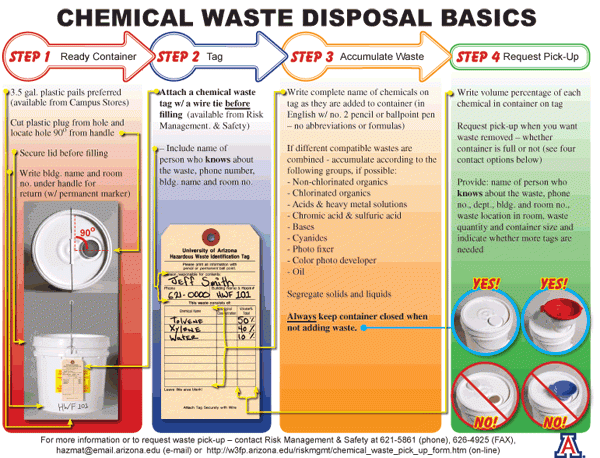
You may not realize it, but proper waste disposal is a critical issue that affects all of us. From household trash to industrial waste, the way we handle and dispose of our garbage has a significant impact on the environment and public health. That’s where MI comes in. MI is a leading provider of expert solutions for proper waste disposal. With years of experience and a team of skilled professionals, MI offers comprehensive waste management services that ensure safe and environmentally-friendly disposal of all types of waste. Whether you are a homeowner, a business owner, or a government agency, MI has the expertise and resources to help you dispose of your waste responsibly and efficiently. Say goodbye to waste management worries and hello to a cleaner, greener future with MI.

Methods of Waste Disposal
Landfill
One of the most common methods of waste disposal is landfilling. Landfills are designated areas where waste materials are disposed of by burying them underground. This method involves depositing waste into excavated pits, which are then covered with soil to minimize odor and prevent the spread of diseases.
Incineration
Incineration is a waste disposal method that involves the combustion of waste materials at high temperatures. This process reduces the volume of waste by converting it into ash, gas, and heat. Incineration can be a viable option for certain types of waste that cannot be recycled or composted.
Composting
Composting is a natural and environmentally friendly method of waste disposal that involves the decomposition of organic materials, such as food scraps and yard waste, into nutrient-rich compost. This process not only diverts organic waste from landfills but also produces a valuable soil amendment that can improve soil fertility and plant growth.
Recycling
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into reusable materials. Through recycling, valuable resources are conserved, and the amount of waste sent to landfills is reduced. Common materials that can be recycled include paper, plastic, glass, and metal.
Waste-to-Energy
Waste-to-Energy is a method of waste disposal that involves converting waste materials into usable forms of energy, such as electricity, heat, or fuel. This process not only helps reduce the volume of waste but also generates renewable energy, which can contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
Challenges in Waste Disposal
Environmental Impact
One of the major challenges in waste disposal is its environmental impact. Improper waste management can lead to air pollution, water pollution, soil contamination, and ecological disruption. The release of greenhouse gases from landfills and incineration facilities also contributes to climate change.
Health Hazards
Inadequate waste disposal practices can pose significant health hazards to both humans and the environment. Exposure to hazardous waste can result in respiratory problems, skin diseases, and other adverse health effects. It is crucial to handle and dispose of hazardous waste materials properly to protect public health and safety.
Resource Depletion
The improper disposal of waste can lead to the depletion of valuable resources. When recyclable materials are sent to landfills instead of being recycled, the opportunity to conserve and reuse those resources is lost. Proper waste disposal methods, such as recycling and waste-to-energy, help recover valuable resources and reduce the strain on natural resource reserves.
Socioeconomic Issues
Waste disposal can also present socioeconomic challenges. Inadequate waste management practices can lead to the creation of informal waste disposal sites, often in marginalized communities, which can have adverse social and economic impacts. Additionally, the cost of waste disposal and the need for proper infrastructure can pose financial burdens on communities and municipalities.
Landfill Management
Site Selection
Choosing an appropriate site for landfills is essential to minimize the environmental impact of waste disposal. Factors such as proximity to water bodies, population centers, and sensitive ecological areas need to be considered when selecting a landfill site. Adequate infrastructure, including access roads and utilities, should also be available.
Waste Compaction
An important aspect of landfill management is waste compaction. Compacting the waste helps reduce its volume, allowing more waste to be accommodated in a given space. This process involves the use of heavy machinery to compress the waste and improve the overall efficiency of the landfill.
Leachate Treatment
Leachate is the liquid that drains from landfills as waste decomposes. It contains various contaminants and pollutants that can contaminate nearby groundwater and surface water bodies. Proper leachate management involves collection, treatment, and disposal of leachate to prevent environmental contamination.
Gas Recovery
Landfills produce methane gas, which is a potent greenhouse gas. To mitigate its environmental impact, gas recovery systems can be implemented to collect and utilize the methane gas for energy generation. This helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and harness the energy potential of landfill gas.
Land Rehabilitation
Once a landfill reaches its capacity, proper land rehabilitation measures should be undertaken to restore the site and minimize its long-term impact. This can include activities such as soil restoration, reforestation, and the establishment of green spaces. Land rehabilitation promotes biodiversity, enhances landscape aesthetics, and transforms former landfills into valuable community assets.
Incineration Techniques
Mass Burn
Mass burn incineration is the most common type of incineration technique, where mixed waste is combusted at high temperatures. This method is suitable for large quantities of waste but may release more air pollutants compared to other incineration techniques.
Moving Grate
Moving grate incineration involves the continuous movement of waste on a grate as it is burned. This method allows for greater control over combustion and better waste sorting capabilities. It is commonly used for municipal solid waste incineration.
Fluidized Bed
Fluidized bed incineration is a technique that involves suspending waste particles on a bed of heated sand or other inert materials. This method ensures better mixing and combustion efficiency, resulting in reduced air emissions and improved energy recovery.
Gasification
Gasification is a thermochemical process that converts waste into a combustible gas called syngas. This gas can be used for energy generation or further processed into liquid fuels. Gasification offers higher energy recovery rates and lower emissions compared to traditional incineration methods.
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that converts waste into solid, liquid, and gaseous products. It operates under oxygen-limited conditions, resulting in the production of biochar, bio-oil, and syngas. Pyrolysis can be an effective way to convert certain types of waste, such as biomass and plastic, into valuable energy resources.

Benefits of Composting
Organic Waste Diversion
Composting organic waste diverts it from landfills, reducing the amount of waste that decomposes and produces methane gas. By composting organic materials such as food scraps and yard waste, valuable nutrients are returned to the soil, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
Soil Enrichment
Compost is a nutrient-rich soil amendment that improves soil fertility and structure. It enhances the water-holding capacity of soil, promotes beneficial microbial activity, and provides essential nutrients for plant growth. The use of compost can lead to healthier and more productive crops and gardens.
Reduced Landfill Use
Composting decreases the amount of organic waste that ends up in landfills. By diverting organic materials to composting facilities, the lifespan of landfills can be extended. This helps preserve valuable land resources and minimizes potential environmental contamination associated with landfills.
Greenhouse Gas Mitigation
When organic waste decomposes in landfills, it produces methane – a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. Composting organic waste instead of landfilling it reduces the production and release of methane into the atmosphere. By minimizing methane emissions, composting helps mitigate climate change impacts.
Community Engagement
Composting encourages community engagement and environmental awareness. It provides opportunities for individuals, schools, and community organizations to actively participate in waste reduction efforts. Composting can also foster a sense of environmental responsibility and promote sustainable practices within communities.
Recycling Strategies
Material Sorting
Material sorting is a critical step in recycling processes. It involves separating different types of waste materials, such as paper, plastic, glass, and metal, to facilitate their proper processing and recycling. Advanced sorting technologies, such as optical sensors and magnetic systems, enable efficient and accurate material separation.
Processing Techniques
After material sorting, various processing techniques are employed to transform waste materials into reusable materials. These techniques include shredding, grinding, melting, and refining, depending on the type of material being recycled. The processed materials are then used as feedstock for new products.
Closed-Loop Recycling
Closed-loop recycling, also known as circular recycling, involves recycling materials to produce the same or similar products repeatedly. This approach reduces the demand for virgin materials, conserves resources, and minimizes waste generation. Closed-loop recycling strives to create a sustainable and circular economy.
Extended Producer Responsibility
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a policy approach that holds producers accountable for the entire life cycle of their products, including their end-of-life management. This encourages manufacturers to design products that are easier to recycle and promotes their active involvement in recycling and waste management initiatives.
Public Awareness
Effective recycling strategies require public awareness and participation. Educational campaigns, recycling incentive programs, and accessible recycling infrastructure can increase public engagement and encourage individuals and businesses to adopt recycling practices. Public awareness is key to achieving high recycling rates and creating a culture of responsible waste management.

Advantages of Waste-to-Energy
Energy Generation
Waste-to-Energy technologies harness the energy content of waste materials to generate electricity, heat, or fuel. By converting waste into usable energy, these technologies contribute to diversifying energy sources and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Waste-to-Energy facilities can produce significant amounts of energy from waste that would otherwise be buried in landfills.
Reduced Emissions
Waste-to-Energy facilities help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by preventing the release of methane gas from landfills and offsetting the need for fossil fuel-based energy generation. Properly designed and operated facilities minimize air pollutants and control emissions, ensuring they meet strict environmental standards and regulations.
Waste Volume Reduction
Waste-to-Energy processes significantly reduce the volume of waste that would otherwise occupy valuable landfill space. The conversion of waste into energy greatly reduces the need for additional landfills and allows for more efficient waste management.
Resource Recovery
Waste-to-Energy technologies often incorporate resource recovery systems that extract valuable materials from the waste stream. These materials, such as metals and recyclable plastics, can be sorted and recycled, contributing to circular economy principles and conserving natural resources.
Renewable Energy Source
Waste-to-Energy is considered a renewable energy source because it utilizes waste materials that would otherwise decompose and produce methane – a potent greenhouse gas. By capturing the energy content of waste, it helps reduce reliance on non-renewable resources and contributes to a more sustainable energy mix.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Air Pollution
Waste disposal methods can result in air pollution through the release of pollutants such as greenhouse gases, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter. Effective waste management practices, such as proper incineration techniques, emission control systems, and waste-to-energy technologies, help minimize air pollution and ensure compliance with air quality standards.
Water Pollution
Improper waste disposal can lead to water pollution through the leaching of contaminants into groundwater and the discharge of waste into surface water bodies. Landfill management practices, leachate treatment systems, and stringent regulatory measures are crucial in preventing water pollution and protecting aquatic ecosystems.
Soil Contamination
Inadequate waste disposal practices can lead to soil contamination due to the release of toxic substances into the soil. Proper waste management techniques, soil remediation measures, and the use of environmentally friendly disposal methods, such as composting and recycling, help prevent soil contamination and preserve agricultural and ecological lands.
Ecological Disruption
Improper waste disposal can disrupt ecosystems by degrading habitats, harming wildlife, and reducing biodiversity. Environmentally conscious waste management practices, such as proper landfill site selection, land rehabilitation efforts, and the promotion of recycling and composting, aid in preserving ecosystems and maintaining ecological balance.
Climate Change
The disposal of waste contributes to climate change through the release of greenhouse gases, particularly methane from landfills. Implementing waste management strategies that reduce methane emissions, such as increased recycling, composting, and waste-to-energy conversion, can help mitigate climate change impacts and foster a more sustainable future.

Health and Safety Measures
Protective Equipment
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential for workers involved in waste disposal activities. This includes gloves, masks, goggles, and other protective gear to prevent exposure to hazardous substances and ensure worker safety.
Hazardous Waste Handling
Handling hazardous waste requires specialized training and precautions to minimize health risks. Proper containment, labeling, and disposal procedures are crucial to prevent accidental spills, contamination, and exposure to potentially harmful substances.
Training and Education
Training and education programs are essential to ensure that waste disposal workers understand proper waste handling procedures, safety protocols, and the importance of following regulations. Ongoing training helps maintain a culture of safety and promotes best practices in waste management.
Monitoring Systems
Monitoring systems, such as air quality monitors and leachate collection systems, are key to identifying potential hazards and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Continuous monitoring helps detect any deviations or issues promptly, allowing for prompt corrective action to protect both workers and the environment.
Emergency Response
Waste disposal facilities should have robust emergency response plans and procedures in place to handle unforeseen incidents, such as spills, fires, or hazardous material releases. By having trained emergency response teams and comprehensive response plans, the risks associated with waste disposal can be minimized, and timely actions can be taken to protect public health and safety.
Technological Innovations
Smart Waste Management
Smart waste management systems utilize advanced technologies, such as sensors, data analytics, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, to optimize waste collection, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. These systems can track waste levels in bins, optimize collection routes, and provide real-time data for better waste management decision-making.
Sensor-Based Solutions
Sensor-based solutions play a vital role in waste management by providing real-time data on waste characterization, sorting, and monitoring. Optical sensors, near-infrared spectroscopy, and other advanced sensing technologies enable accurate waste sorting, quality control, and waste stream analysis for improved recycling and resource recovery.
Waste Analytics
Waste analytics involves the use of data mining and analytics techniques to analyze waste management-related data, such as waste generation trends, recycling rates, and material flow analysis. This data-driven approach helps identify areas for improvement, optimize waste management processes, and make informed policy decisions.
Robotic Systems
Robotic systems are increasingly being utilized in waste management operations, such as waste sorting and recycling. These automated systems can efficiently segregate different types of waste, improving recycling rates and reducing the need for manual labor. Robotics also enhance safety by reducing human exposure to hazardous materials.
Blockchain Applications
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize waste management by improving transparency, traceability, and accountability in waste disposal processes. Blockchain can help track and record waste transactions, certifications, and waste flow, ensuring that waste is handled responsibly and in compliance with regulations.
In conclusion, proper waste disposal is essential for environmental sustainability and public health. Landfilling, incineration, composting, recycling, and waste-to-energy are different methods that can be used based on the characteristics of the waste and the desired outcomes. However, challenges such as environmental impact, health hazards, resource depletion, and socioeconomic issues need to be addressed through effective waste management strategies. Landfill management techniques, appropriate incineration methods, composting benefits, recycling strategies, and waste-to-energy advantages offer opportunities for efficient waste disposal. Environmental impact assessments, health and safety measures, and technological innovations play crucial roles in ensuring proper waste management practices are implemented for a healthier and more sustainable future.