When it comes to managing your household waste, the question of where pee goes might not be something you often think about. However, understanding whether or not pee should go in a septic tank is an important aspect of maintaining a healthy and efficient system. In this article, we will shed light on this commonly asked question and provide you with some key insights to help you make the right decisions for your septic tank. So, let’s get started!
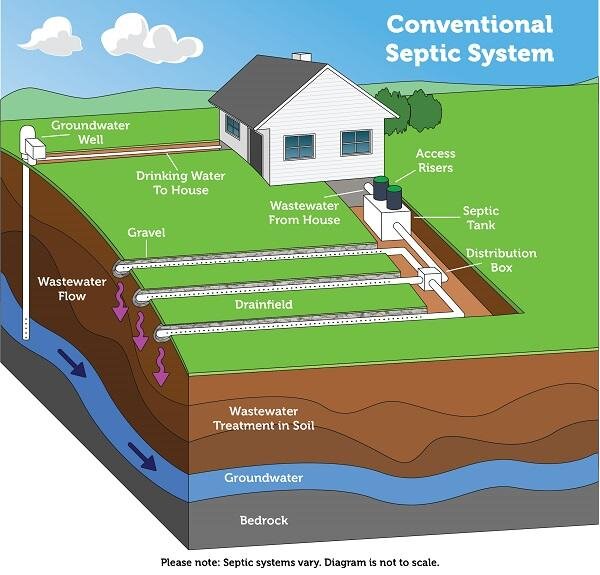
What is a septic tank?
Definition
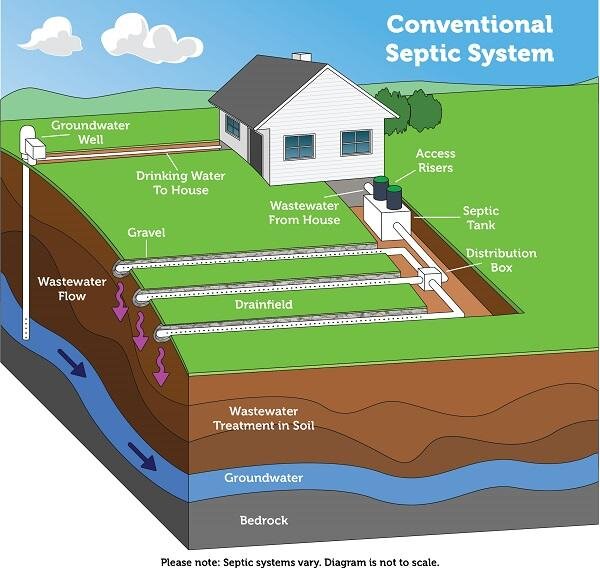
A septic tank is a large underground container made of concrete, fiberglass, or polyethylene that is used to treat wastewater from households that are not connected to a centralized sewer system. It provides an on-site sewage disposal system by separating solid waste and allowing the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the wastewater before it is discharged into the environment.
Function
The primary function of a septic tank is to treat and store wastewater from a property. It allows for the separation of solids, which settle at the bottom of the tank, from liquids and scum, which float to the top. This separation process allows the liquid, known as effluent, to drain out of the septic tank into a drain field or leach field, where it can be naturally filtered by the soil.
Components
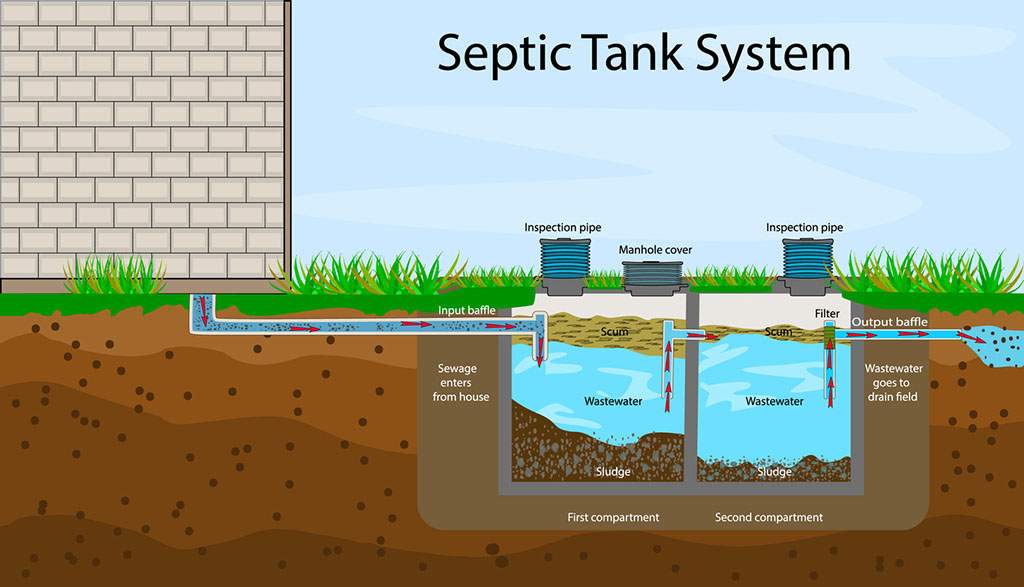
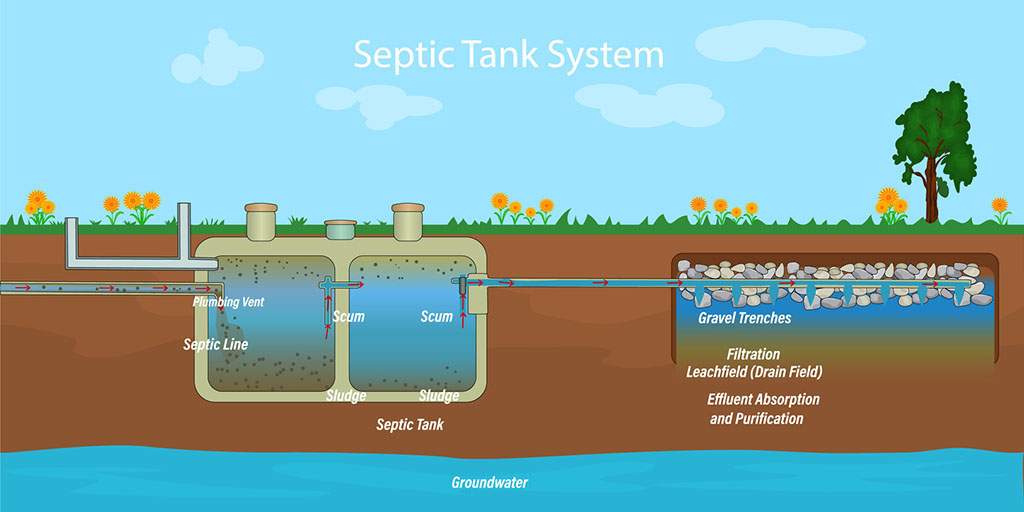
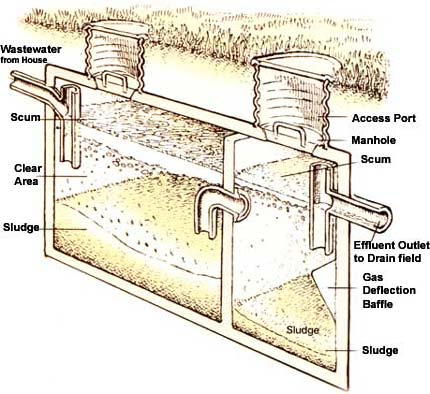
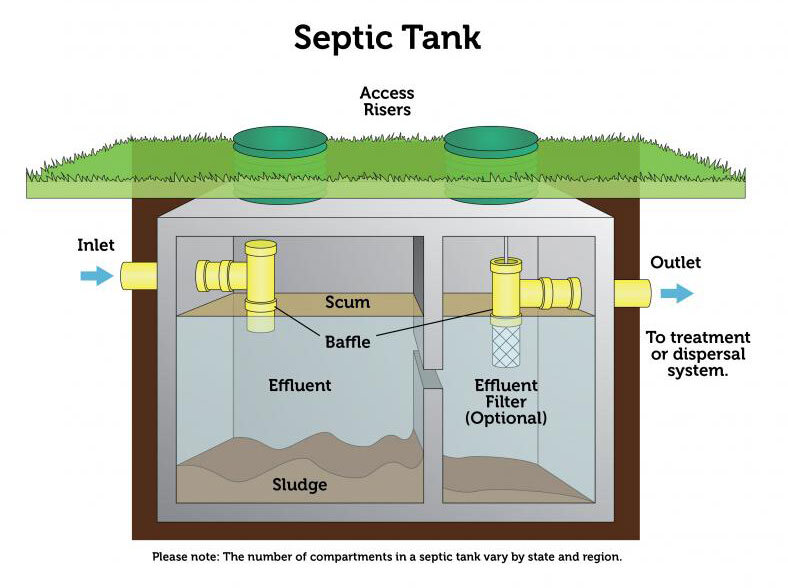
A septic tank consists of several key components that work together to ensure proper wastewater treatment. These components include an inlet pipe through which wastewater enters the tank, baffles that prevent solids from entering the outlet pipe, a settling chamber where solid waste settles, a scum layer made up of oils and fats that float on top of the wastewater, and an outlet pipe for the effluent to exit the tank.
What happens in a septic tank?
Waste separation
When wastewater enters a septic tank, it undergoes a process of waste separation. Solid waste, such as toilet paper and other organic matter, sinks to the bottom and forms a layer of sludge. Greases and oils, collectively known as scum, float to the top, forming a layer that helps trap odors and prevent them from escaping into the air.
Microbial breakdown
Within the septic tank, naturally occurring bacteria and other microorganisms break down the organic matter present in the wastewater. These microbes play a crucial role in the decomposition process, breaking down complex organic compounds into simpler forms. This microbial breakdown helps to reduce the volume of solids in the tank and promotes the formation of gases, such as methane and carbon dioxide.
Sludge accumulation
Over time, the sludge layer at the bottom of the septic tank gradually accumulates. This sludge is comprised of undigested organic matter and heavy solids that settle over time. While a certain amount of sludge is normal and expected, excessive accumulation can lead to operational problems and must be managed through regular pumping and maintenance.
Effluent drainage
Once the microbial breakdown and waste separation processes have taken place, the remaining liquid, known as effluent, drains from the septic tank through the outlet pipe. This effluent then undergoes further treatment in the drain field, where it is naturally filtered and treated by the soil, before returning to the groundwater system.
Can you put pee in a septic tank?
Human urine composition
Human urine is primarily composed of water, with approximately 95% water content. It also contains small amounts of urea, a nitrogenous waste product, and various dissolved salts, such as sodium and potassium.
Impact of urine on septic tank
Urine, when mixed with other wastewater in a septic tank, does not harm the overall functioning of the system. In fact, urine can provide additional liquid volume, which aids in the proper decomposition of solid waste. The small amount of nitrogen present in urine can also contribute to the overall nutrient balance in the tank.
Amount of urine produced
On average, an adult produces about 1 to 2 liters of urine per day. With a properly sized septic tank, the addition of urine to the wastewater volume should not pose any significant issues. However, if there is excessive urine production or an undersized septic tank, it can lead to an imbalance in the system and may require more frequent maintenance and pumping.
Proper urine disposal
While urine can be safely disposed of in a septic tank, it is worth considering alternative methods of urine disposal. Diverting urine from the septic tank and using it separately, such as for fertilizing plants, can have several benefits. It reduces the strain on the septic system, promotes water conservation, and allows for the reuse of nutrients in urine as a natural fertilizer.
Urine vs. feces in septic tanks
Different compositions
Urine and feces have different compositions and can have varying effects on septic tank performance. Feces contain higher levels of organic matter, fats, and solids, which can contribute to sludge accumulation in the tank. Urine, on the other hand, is mostly liquid and contains fewer solids.
Effects on septic tank
The presence of feces in a septic tank requires a longer retention time for decomposition due to the higher organic content. This can lead to increased sludge buildup and increased maintenance needs. Urine, with its higher liquid content, can help in the decomposition process and facilitate the proper functioning of the septic tank.
Septic tank size requirements
The volume of urine and feces produced by a household can vary significantly. Larger households with more occupants will naturally produce a greater amount of both urine and feces. To ensure the proper functioning of a septic tank, it is crucial to have an adequately sized tank that can handle the expected waste volume.
How to maintain a healthy septic tank
Regular pumping
Regular pumping is essential for maintaining a healthy septic tank. The frequency of pumping depends on factors such as tank size, household size, and water usage. Typically, it is recommended to have a septic tank pumped every 3 to 5 years to remove accumulated sludge and prevent potential issues with the system.
Avoiding excessive water usage
Excessive water usage can put a strain on a septic tank, leading to an overburdened system. It is important to conserve water and avoid unnecessary water usage, such as excessively long showers or running water continuously. Conserving water not only helps to maintain a healthy septic tank but also reduces overall water consumption.
Proper waste disposal
To ensure the proper functioning of a septic tank, it is crucial to be mindful of what is being flushed or poured down the drain. Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items, such as diapers, sanitary products, or household chemicals, as these can clog the system and interfere with the microbial breakdown process. Only dispose of biodegradable materials that can be easily decomposed by the natural processes within the septic tank.
Maintenance schedule
Establishing a regular maintenance schedule for your septic tank is important in preventing potential issues and ensuring its long-term functionality. Keep a record of pumping dates, inspections, and any maintenance or repairs that have been conducted. This record will help you stay on top of necessary maintenance tasks and allow for proper monitoring of the septic system’s health.
Effects of excessive urine in septic tanks
Increased liquid volume
Excessive urine in a septic tank can lead to an increased liquid volume, which may exceed the design capacity of the tank. This can overwhelm the system and disrupt the balance of solids, liquids, and microbial activity within the tank. It is therefore important to ensure that the septic tank is adequately sized for the expected wastewater volume.
Imbalance in microbial activity
Microbes play a vital role in the breakdown of organic matter within a septic tank. Excessive urine can upset the balance of microbial activity, potentially leading to a reduction in the breakdown of solids and an increased accumulation of sludge. This imbalance can compromise the overall effectiveness and efficiency of the septic tank.
Sludge buildup prevention
Sludge buildup is an inevitable occurrence in septic tanks, but excessive urine can exacerbate the problem. To prevent excessive sludge accumulation, regular pumping and maintenance become even more crucial. Keeping a balanced microbial ecosystem and removing excess sludge through proper maintenance practices will help prevent clogging and costly repairs.
Consequences of improper urine disposal
Contamination of surrounding areas
Improper urine disposal, such as direct discharge onto the ground or into nearby water sources, can lead to the contamination of surrounding areas. Urine contains various salts and nutrients, including nitrogen and phosphorus, which can contribute to the pollution of surface water or groundwater. This contamination can have detrimental effects on the environment and local ecosystems.
Groundwater pollution
If urine finds its way into groundwater sources due to improper disposal practices, it can contaminate drinking water supplies. Groundwater pollution caused by urine can pose serious health risks to both humans and wildlife. It is essential to follow proper urine disposal methods to ensure the protection of groundwater resources.
Potential health risks
Improper urine disposal practices can present health risks to individuals who come into contact with contaminated water sources or surfaces. Exposure to pathogens and harmful bacteria present in urine can lead to illnesses and infections. To protect both personal health and the health of the community, it is crucial to dispose of urine responsibly.
Alternative urine disposal methods
Composting toilets
Composting toilets are an alternative method of urine disposal that separate urine from solid waste. These toilets use a dual-chamber system, allowing for the proper decomposition of solid waste while diverting urine into a separate container. The separated urine can then be safely stored and used as a natural fertilizer.
Greywater systems
Greywater systems can be used to divert urine from septic tanks. Greywater refers to wastewater generated from sources other than toilets, such as sinks, showers, and laundry. By separating urine from greywater, it is possible to direct the urine to a separate storage or treatment system, reducing the load on the septic tank.
Urine-diverting toilets
Urine-diverting toilets, commonly used in eco-friendly and sustainable housing designs, are specifically designed to separate urine from solid waste. These toilets have separate compartments for urine and solid waste, allowing for the collection and disposal of urine separately from the septic system. The diverted urine can be treated or used as a valuable nutrient resource.
Benefits of diverting urine from septic tanks
Reduced strain on septic system
Diverting urine from septic tanks can significantly reduce the strain on the system. By separating urine, the overall wastewater volume entering the septic tank is decreased, allowing for better management of solids and more efficient microbial breakdown. This reduces the need for frequent maintenance and reduces the risk of system overload.
Reuse of urine as fertilizer
Urine is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential nutrients for plant growth. By diverting urine from septic tanks and using it as a natural fertilizer, these nutrients can be returned to the soil, promoting healthy plant growth and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. This sustainable practice contributes to environmental conservation and resource management.
Decreased water consumption
Diverting urine from septic tanks also promotes water conservation. With the reduced wastewater volume entering the septic tank, less water is required for flushing, resulting in decreased water consumption overall. This is especially beneficial in areas facing water scarcity or regions where efficient water management is a priority.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of urine in septic tank systems is crucial for maintaining a healthy and efficient wastewater management system. While urine can be safely disposed of in septic tanks, alternative methods such as composting toilets, greywater systems, and urine-diverting toilets offer numerous benefits, including reduced strain on the septic system, reuse of urine as fertilizer, and decreased water consumption. Responsible urine disposal practices not only protect the environment and groundwater sources but also contribute to sustainable water and waste management. By implementing proper maintenance strategies and considering alternative urine disposal methods, you can help ensure the longevity and effectiveness of your septic tank system while minimizing environmental impacts.